Next Level AM
Status: During employment as an architect & researcher at ITE TUBS.
Project: Next Level AM explores the potential of additive manufacturing in the AEC sector.
Location: Germany, Denmark, Switzerland.
Client: Eurostars Europ.
Key information:
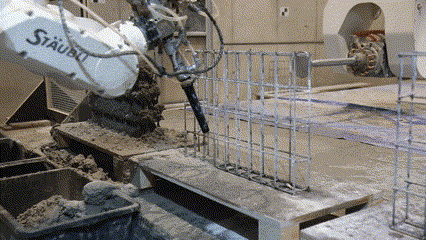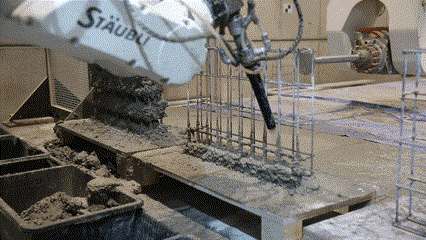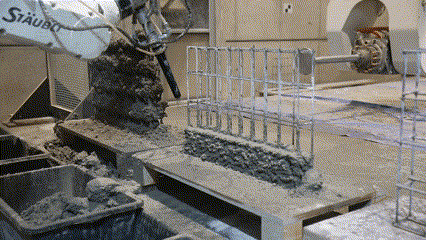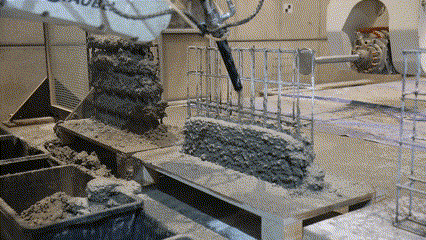
Next Level AM is a Eurostars research project, in collaboration with MESH AG (an ETH Zurich spin-off) and COBOD International. The project develops automated methods for building robotically reinforced concrete walls.
Services:
Research & development.
Objective
The Next Level AM project, funded by Eurostars, had aimed to advance additive manufacturing in construction by developing an automated system for producing robotically reinforced concrete walls. In collaboration with MESH AG (an ETH Zurich spin-off specializing in robotic wire reinforcement) and COBOD International (a leader in construction 3D printing), the project had combined digital design, robotic fabrication, and reinforcement technology to push the boundaries of Construction 4.0, enhancing precision, efficiency, and sustainability in the AEC industry.
Experement design
The Next Level AM project had followed an experimental, research-driven methodology to explore how additive manufacturing could be applied to multi-storey mixed-use construction. The approach had combined digital design development, material research, and robotic fabrication testing to establish a fully integrated workflow for producing robotically reinforced concrete walls. At the start, the project partners had developed parametric design models to adapt building geometries to printing and reinforcement constraints. Simultaneously, material and reinforcement experiments had been conducted to optimize printable concrete mixes and wire reinforcement systems.
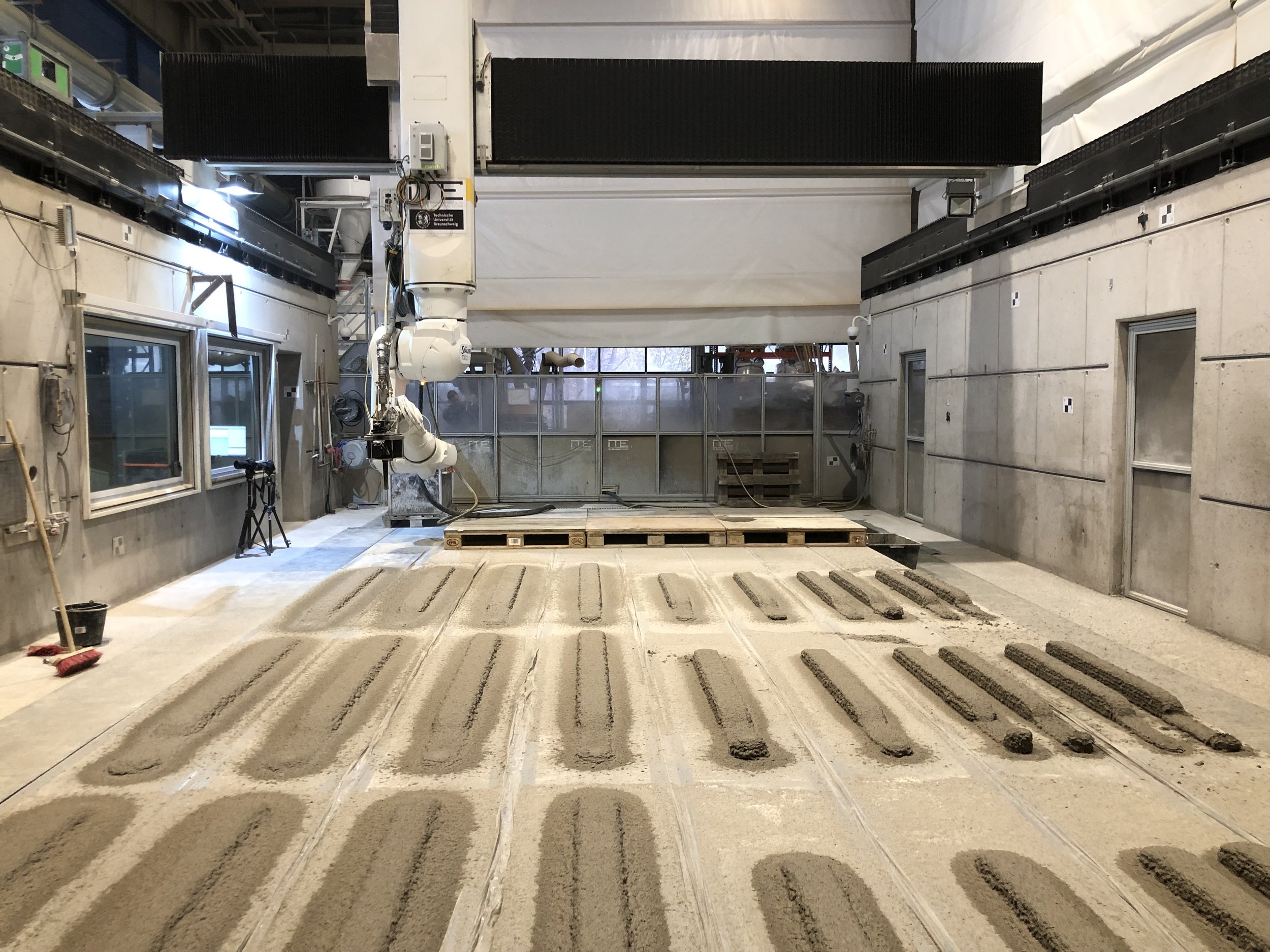
Fabrication
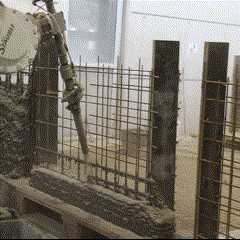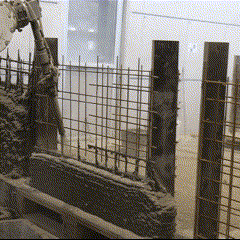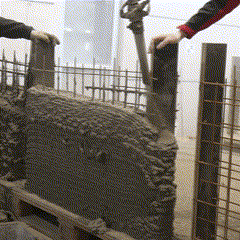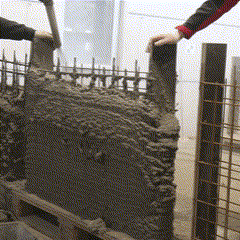
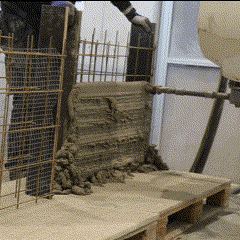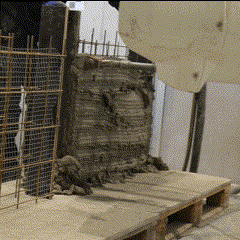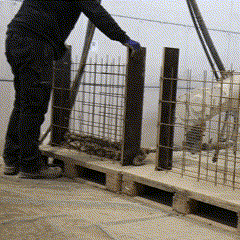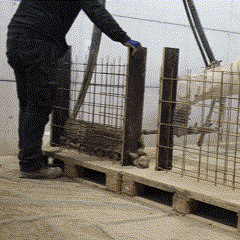
Fabrication has been validated through prototype fabrication at various scales, where robotic printing and reinforcement processes had been tested in coordination between MESH AG, COBOD International, and RUPP Gebäudedruck.
Each prototype had undergone structural and material testing, including load-bearing, bonding, and durability assessments. The results had been used to refine the digital-to-physical workflow, ensuring that design data, printing parameters, and robotic operations worked seamlessly together. Through this iterative process, the project had demonstrated the feasibility of automated, reinforced additive manufacturing as a scalable solution for efficient, sustainable, and adaptable urban construction within the framework of Construction 4.0.
Copenhagen AM
The Copenhagen AM studio had provided students with a hands-on research environment to explore digital design and robotic fabrication in architecture. Through collaborative experimentation with additive manufacturing and computational design, students had developed innovative prototypes and architectural concepts that illustrated the potential of automated construction technologies. The studio had aimed to reshape architectural education by bridging academic learning with real-world digital practice, preparing the next generation of designers for the challenges and opportunities of Construction 4.0.